Eye presentations make up to around 6% of all presentations to the ED. During the day we have the West of England Eye unit (WEEU) and suitable patients are referred to the eye triage line for assessment. However Ophthalmology is an important subject in which you should develop your skills, especially for emergency department doctors and GPs.
We are lucky to have an eye room in the ED complete with slit lamp, Snellan chart, tonometer and eye trolley with important eye drops that will aid in assessment and treatment of common eye emergencies.
It is widely understood that new Drs to the ED often feel uneasy when presented with eye complaints. However with the resources below created by Dr Jamie East and Dr Rachel Wilson You will better equip to assess eye emergencies giving you a foundation to build on with further clinical exposure and learning opportunities on the shop floor.
We are lucky to have an eye room in the ED complete with slit lamp, Snellan chart, tonometer and eye trolley with important eye drops that will aid in assessment and treatment of common eye emergencies.
It is widely understood that new Drs to the ED often feel uneasy when presented with eye complaints. However with the resources below created by Dr Jamie East and Dr Rachel Wilson You will better equip to assess eye emergencies giving you a foundation to build on with further clinical exposure and learning opportunities on the shop floor.
snellen chart
Visual acuity is said to be the vital sign of the eye and any patient presenting with an eye complaint should have a visual acuity documented.
Please become familiar with the Snellen chart currently in room L131 (The Eye Room)
Visual acuity (VA) should be documented as: distance tested (6m) / best optotype read. I.E 6/6 is normal vision but a patient may have a visual acuity of 6/12 or 6/24 depending on the best complete line read.
Refractory errors can be corrected with use of a pinhole eye cover.
Please become familiar with the Snellen chart currently in room L131 (The Eye Room)
Visual acuity (VA) should be documented as: distance tested (6m) / best optotype read. I.E 6/6 is normal vision but a patient may have a visual acuity of 6/12 or 6/24 depending on the best complete line read.
Refractory errors can be corrected with use of a pinhole eye cover.
slit lamp
The slit lamp allows the clinician to magnify the eye to inspect it in closer detail, and with flouroscene corneal defects can be appreciated. Its also allows assessment of the anterior chamber of the eye which can help differentiate between causes of a red, painful eye.
See below for a tutorial on how to set up and use the slit lamp:
See below for a tutorial on how to set up and use the slit lamp:
SEtting up the slit lamp
examining the eye using a slit lamp
measuring intraoccular pressure
Some emergency causes of eye pain can present with increased intraoccular pressure, two important causes that can threaten sight include Acute-closed angle closure glaucoma and retrobulbar haematoma ( A history of trauma and/or increased bleeding tendencies are important here). The increased pressure in the eye can cause irreversible optic nerve ischaemia leading to blindness.
We can measure the intraoccular pressure of the eye using a tonometer. This is usually done by an ophthalmologist but it is important to know how to use one in case of an emergency or with a delay to ophthalmology input.
A normal intraoccular pressure in 10-21mmHg.
We can measure the intraoccular pressure of the eye using a tonometer. This is usually done by an ophthalmologist but it is important to know how to use one in case of an emergency or with a delay to ophthalmology input.
A normal intraoccular pressure in 10-21mmHg.
corneal foreign body
A corneal foreign body is a common cause of a sudden painful, red eye and a thorough history will often reveal the likely source of foreign body, i.e sudden pain whilst welding, gardening etc.
Local anaesthetic eye drops will numb the eye and stop the irritation allowing a thorough assessment using the slit lamp. (see common eye medications below)
Now you can see the foreign body, removing it is the next challenge. Some can be simply brushed off with a damp cotton bud but others such as metal foreign bodies will often need a more delicate removal with a needle. If a metal foreign body has been on the cornea for some time it may start to oxidise and form a deeper 'rust ring'. In this instance although the metal foreign body can be removed the "rust ring" may need further treatment using a Burr drill, the patient will have to be referred to the WEEU urgently (The next morning if overnight) for this to be carried out.
Please give the patient some Occ. Chloramphenicol 1% to take away and use QDS until their appointment in WEEU, this will make the metal FB easier to remove
Please watch the video below for an expert tutorial of foreign body removal.
Local anaesthetic eye drops will numb the eye and stop the irritation allowing a thorough assessment using the slit lamp. (see common eye medications below)
Now you can see the foreign body, removing it is the next challenge. Some can be simply brushed off with a damp cotton bud but others such as metal foreign bodies will often need a more delicate removal with a needle. If a metal foreign body has been on the cornea for some time it may start to oxidise and form a deeper 'rust ring'. In this instance although the metal foreign body can be removed the "rust ring" may need further treatment using a Burr drill, the patient will have to be referred to the WEEU urgently (The next morning if overnight) for this to be carried out.
Please give the patient some Occ. Chloramphenicol 1% to take away and use QDS until their appointment in WEEU, this will make the metal FB easier to remove
Please watch the video below for an expert tutorial of foreign body removal.
A video demonstrating the removal of a foreign body as seen through a slit lamp can be seen here
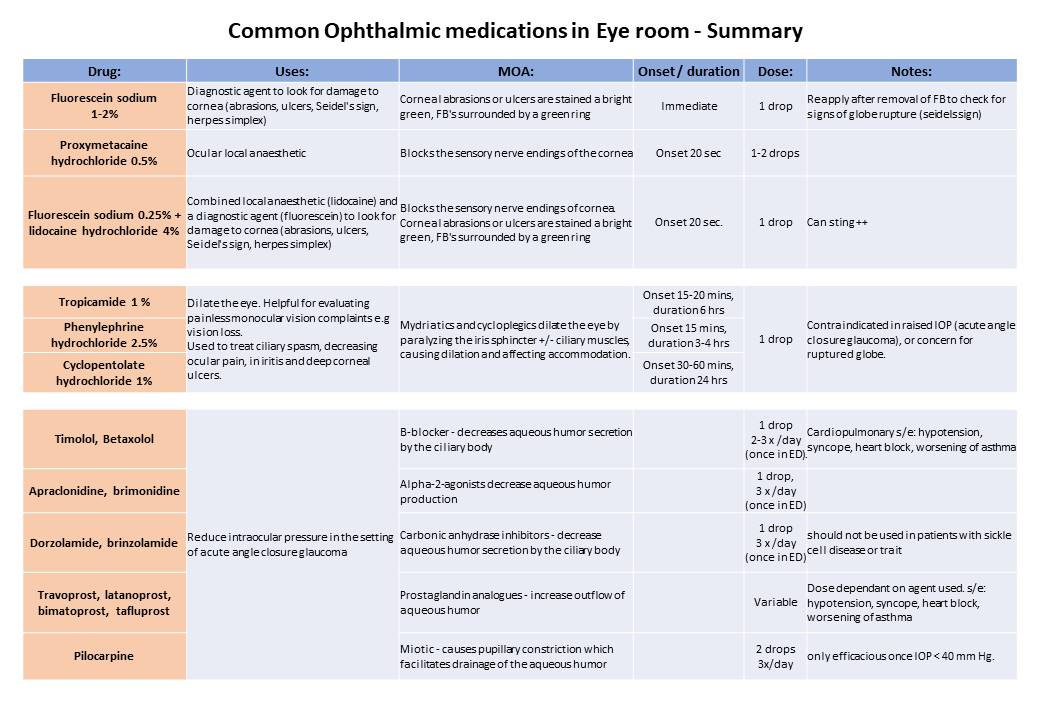
Common drugs used to treat ophthalmological emergencies
You have watched demostrations on how to use the examination equipment in the eye room and been shown a brief summary of what medications can be helpful when treating emergency eye complaints. Please make sure that the first time you use the equipment or any new medications that you seek senior help and supervision.
Lateral canthotomy
Lateral canthotomy is a required skill for the emergency physician. It is a procedure that allows decompression of orbital apex syndrome (orbital compartment syndrome usually caused by retrobulbar haemorrhage or orbital cellulitis)
Facial trauma and suspected orbital compartment syndrome. Signs include:
Equipment
Facial trauma and suspected orbital compartment syndrome. Signs include:
- Proptosis
- Restricted eye movements
- markedly reduced visual acuity
- High intraocular pressure (using tonometer, or comparing both eyes with palpation from a finger of thumb)
- Subconjunctival haemorrhage
- swollen and bruised lids
- Relative afferent pupilary defect (RAPD)
Equipment
- Chloraprep applicator
- Lidocaine 1% with needle and syringe
- Tenotomy scissors
- Straight artery forceps
Further resources
Please find below some useful resources for improving your knowledge of emergency eye complaints and causes of painful, red eyes or visual loss:
RCEM Learning - Atraumatic red eye
RCEM Learning - Sudden visual loss
RCEM Learning - orbital apex syndrome or retrobulbar haematoma 'A sight for sore eyes
RCEM Learning - corneal injuries
RCEM Learning - Sight for sore eyes (lateral canthotomy)
RCEM Learning - Atraumatic red eye
RCEM Learning - Sudden visual loss
RCEM Learning - orbital apex syndrome or retrobulbar haematoma 'A sight for sore eyes
RCEM Learning - corneal injuries
RCEM Learning - Sight for sore eyes (lateral canthotomy)